Many of us know Julie Bowen from her memorable roles, especially as Claire Dunphy on "Modern Family," but you might be wondering, what heart condition does Julie Bowen have? It's a question that pops up quite a bit, as she has been open about a health challenge that sometimes impacts her. Learning about public figures and their personal health stories can, in a way, shed light on conditions many people experience but might not openly discuss. So, we're going to take a look at what she's shared.
Her experience offers a really important glimpse into how a specific heart-related condition can affect someone's daily life, even a busy actress. It shows that health challenges can touch anyone, regardless of their public standing. This openness from someone like Julie Bowen, you know, can help others feel less alone if they are dealing with similar situations.
This article will explore the condition Julie Bowen has spoken about, explain what it means, and touch upon how it's typically managed. We'll also, in some respects, cover some general information about your heart and its amazing work. It's a chance to understand a bit more about a common, yet often misunderstood, health concern.
- Real Automovil Club De Espa%C3%B1a
- Why Is My Instagram Not Working
- 111 W 57th St
- Javiers Restaurant Newport Beach Photos
- Nike Sb Jordan 4
Table of Contents
- Who is Julie Bowen? A Quick Look
- Understanding Julie Bowen's Heart Condition
- What is Vasovagal Syncope?
- Common Triggers and What Happens
- Signs and Sensations Before Fainting
- Living with Vasovagal Syncope: Everyday Management
- A Little Bit About Your Heart
- Common Questions About Julie Bowen's Health
- Staying Informed About Your Well-being
Who is Julie Bowen? A Quick Look
Julie Bowen Luetkemeyer is an American actress and director, someone many people recognize instantly. She gained a lot of fame for her role as Claire Dunphy on the television comedy series "Modern Family," a show that ran for many years. Before that, she had notable parts in other TV shows and movies, building a solid career in Hollywood. She's, in a way, known for her energetic performances and comedic timing.
Her career has spanned decades, showing her range in different types of roles. She's a familiar face on screens, and her personal stories, like the one about her health, often resonate with her audience. It's, you know, a part of what makes her so relatable to many people.
| Full Name | Julie Bowen Luetkemeyer |
| Date of Birth | March 3, 1970 |
| Place of Birth | Baltimore, Maryland, U.S. |
| Occupation | Actress, Director |
| Known For | Claire Dunphy in "Modern Family" |
Understanding Julie Bowen's Heart Condition
The heart condition Julie Bowen has openly discussed is called vasovagal syncope. This isn't a heart disease in the traditional sense, like something wrong with the heart muscle itself, but rather a common nervous system response that affects blood flow to the brain. It's, in a way, a reflex that can cause a person to faint.
- Los Angeles Equestrian Center
- Boo Did I Scare You Im A Job Application
- Charles Spencer 9th Earl Spencer
- Noches De Colombia Elizabeth
- John Mulaney Olivia Munn
She has spoken about experiencing fainting spells since she was a teenager, which can be quite startling for anyone. This condition means that her body, under certain circumstances, might react by briefly lowering her heart rate and blood pressure, causing a temporary reduction in blood flow to her brain. This temporary lack of blood flow is what leads to a fainting episode. It's, you know, a pretty quick event, but it can feel disorienting.
For someone in the public eye, managing such a condition can present unique challenges, especially with demanding work schedules and public appearances. It shows, too it's almost, a level of strength to be so open about a personal health matter. Her willingness to share her experience has, apparently, helped many people understand this condition better.
What is Vasovagal Syncope?
Vasovagal syncope, often simply called a common faint, happens when your body overreacts to certain triggers. These triggers can include seeing blood, experiencing intense emotional stress, or standing for a very long time. When this overreaction happens, it causes a sudden drop in your heart rate and blood pressure. This drop means less blood gets to your brain, and that's what makes you pass out. It's, in a way, your body's automatic response.
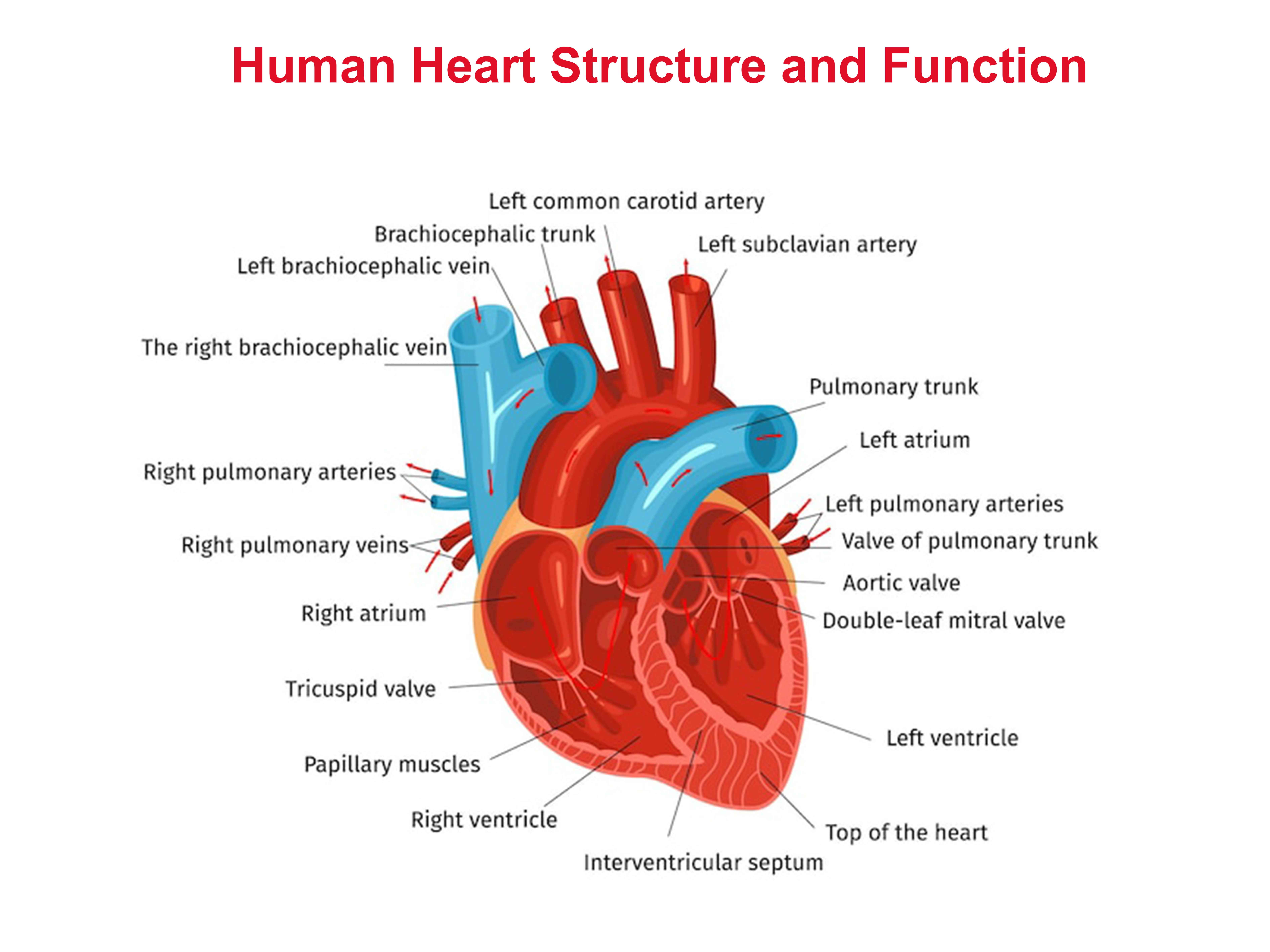
Your heart, as we know, is the main organ of your cardiovascular system, a network of blood vessels that pumps blood throughout your body. It's a vital organ that keeps blood moving. When you have vasovagal syncope, this system, particularly the nerves that control blood vessels and heart rate, gets a mixed signal. This signal tells your blood vessels to widen and your heart rate to slow down, which together reduce blood pressure quite a bit. This is why, you know, you might feel faint.
The heart is a muscular organ that serves as a pump to circulate the blood. It consists of four main chambers: two atria and two ventricles. Normally, it works continuously to collect deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body, carry it to the lungs to be oxygenated and release carbon dioxide, and then pump that oxygenated blood throughout the body. With vasovagal syncope, this smooth process is briefly disrupted, causing the temporary loss of consciousness. It's, actually, a fascinating example of how our body's systems are interconnected.
How the Body Reacts
When a vasovagal episode begins, the vagus nerve, which connects your brain to your heart and digestive system, becomes overstimulated. This nerve plays a big role in controlling your heart rate and blood pressure. When it's overstimulated, it sends signals that cause your blood vessels to relax and widen, particularly those in your legs. This allows blood to pool in your lower body, meaning less blood returns to your heart. Consequently, less blood is pumped up to your brain. This reduction in blood flow to the brain is what causes you to lose consciousness, if only for a short time. It's, basically, a temporary shutdown.
The fainting spell itself is usually very brief, often lasting only a few seconds to a minute or two. Most people recover quickly once they lie down and blood flow to the brain is restored. It's not typically considered a serious condition in terms of causing lasting harm, but the act of fainting can lead to injuries from falling. So, it's something to be aware of, you know, for safety.
Common Triggers and What Happens
Understanding what might set off a vasovagal syncope episode is a big part of managing the condition. Triggers can vary quite a bit from person to person, but some are very common. These might include standing for a long period, especially in a warm environment. Think about standing in a crowded, stuffy room for too long. That, you know, can sometimes do it.
Strong emotional experiences are also common triggers. This could be anything from sudden fear or anxiety to intense pain. Seeing blood or experiencing an injury can also bring on an episode. For some people, even the sight of a needle or the thought of a medical procedure can be enough. It's, in a way, a highly personal response.
Other things that can act as triggers include dehydration, skipping meals, or being very tired. The body's systems need to be in balance, and when they're not, it can make someone more susceptible to an episode. It's, actually, a reminder to take care of yourself. Knowing your specific triggers is, therefore, a very important step in preventing fainting spells.
Signs and Sensations Before Fainting
Before someone with vasovagal syncope faints, they often experience a range of warning signs. These pre-fainting sensations are known as prodromal symptoms, and recognizing them can give a person a chance to prevent a full fainting episode. It's, you know, like a little heads-up from your body.
Common signs that might appear just before an episode include:
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy, like the room is spinning just a little.
- Nausea, which can sometimes be accompanied by stomach discomfort.
- A feeling of warmth or clamminess, perhaps even breaking out in a cold sweat.
- Skin looking pale, as if all the color has drained from your face.
- Blurred vision or seeing spots, almost like your vision is tunneling.
- Feeling unusually weak or tired, like your energy has suddenly left you.
- A ringing in your ears or other unusual sounds.
If someone experiences these signs, the best thing to do is to lie down immediately, if possible, or sit with your head between your knees. This helps to get blood flowing back to the brain more quickly. It's, basically, a simple but effective way to try and avoid passing out completely. Learn more about preventing fainting spells on our site.
Living with Vasovagal Syncope: Everyday Management
Managing vasovagal syncope is mostly about prevention and knowing what to do if you feel an episode coming on. It's about being aware of your body and its signals. For many people, it means making some small adjustments to their daily routines. So, it's not usually about taking medications, but rather about lifestyle choices.
One of the most important things is to stay well-hydrated. Drinking enough water throughout the day can help maintain blood volume and pressure. Avoiding prolonged standing, especially in warm or crowded places, is also a good idea. If you must stand for a while, try to move your legs to help with blood circulation. This, you know, can make a real difference.
Recognizing your personal triggers is, arguably, key. If you know that certain situations or sights tend to make you feel faint, you can try to avoid them or prepare for them. For instance, if blood makes you queasy, you might look away during a blood test. If you start to feel any of the warning signs, lying down with your feet elevated can help blood flow back to your brain. This simple action can often prevent a full faint. It's, actually, a very helpful trick.
Wearing compression stockings might also be suggested for some people, as they can help prevent blood from pooling in the legs. Eating regular meals and avoiding skipping them can also keep your blood sugar stable, which is important for overall well-being. These small steps, in a way, add up to better management of the condition. It's about empowering yourself with knowledge and simple actions.
A Little Bit About Your Heart
Your heart, you know, is a pretty amazing organ. It's basically a pump, always working to move blood around your body. It's about the size of a closed fist, and it sits in your chest, a little to the left, between your lungs. This muscular organ is, in a way, the center of your cardiovascular system. It's a vital organ that keeps blood circulating.
It has four hollow spaces, called chambers, and these are surrounded by muscle and other heart tissue. The chambers are separated by heart tissue. Two of these are atria, and two are ventricles. This whole setup works to collect blood that's low on oxygen from your body, send it to your lungs to pick up oxygen and let go of carbon dioxide, and then pump that fresh
- Delta Passengers Held Up Collapsing Ceiling With Their Hands Mid Flight
- Outrigger Reef Oahu Hawaii
- Trenton Punk Rock Flea Market
- Paris Hilton Malibu Home
- Dita Von Teese Las Vegas

Detail Author:
- Name : Mrs. Dessie Blick
- Username : annie.stroman
- Email : tyson87@stokes.net
- Birthdate : 1994-05-05
- Address : 4732 Deshaun Divide Port Malloryberg, GA 72306-2224
- Phone : +1-559-228-8865
- Company : Ullrich-Gottlieb
- Job : Crane and Tower Operator
- Bio : Blanditiis perferendis voluptates quae adipisci ratione deleniti quas. Vitae sed cumque consequatur alias. Rerum nihil suscipit voluptates in ducimus in.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/reina_rodriguez
- username : reina_rodriguez
- bio : Totam magni quibusdam rerum impedit corrupti alias. Molestias at harum ex earum sapiente. Voluptate explicabo et perspiciatis.
- followers : 285
- following : 280
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/reina_id
- username : reina_id
- bio : Non sit molestiae quam. Perspiciatis repellat qui repellat iste non.
- followers : 1261
- following : 1272

